ORLANDO, FL (February 16, 2018) – The Laser Institute of America is pleased to announce that the 2018 Laser Additive Manufacturing (LAM®) conference will be held at the Schaumburg Convention Center in Schaumburg, IL, March 27–28. For the first time in its 10-year history, the conference will be co-located with the Lasers in Manufacturing Event® […]
Tag: Laser Cladding
Diode Lasers in Cladding, Additive and Hybrid Manufacturing
By Oleg Raykis Today there exist a number of technologies for additive manufacturing of components. The two most prominent types utilizing lasers for generating parts out of metals are either powder bed based solutions or direct energy deposition, often referred to as laser metal deposition. As a company Laserline focuses mainly on the second type. […]
Turbine Blade Cladding & Remelting for Single-Crystal Volume Extension
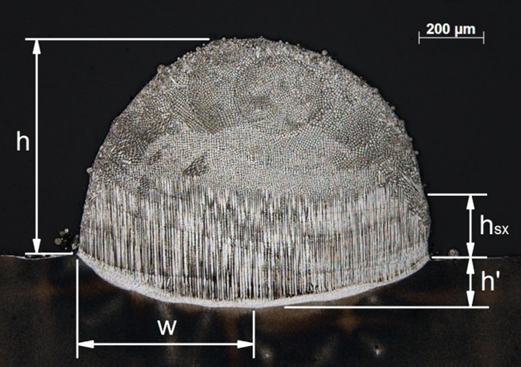
By Irene Alfred, Boris Rottwinkel, Christian Noelke, Volker Wesling, Stefan Kaierle Nickel-based superalloys are used extensively in the combustor and turbine sections of aircraft engines due to their ability to withstand temperatures of up to 1100°C, thereby increasing engine efficiency. The microstructure of single-crystal turbine blades show superior creep and fatigue properties when compared to poly-crystal […]
LAM 2015: Advancing the Applications of Laser Additive Manufacturing Technologies
ORLANDO, FL, Nov. 26, 2014 — The Laser Institute of America (LIA)’s annual workshop on laser additive manufacturing moves to LIA’s hometown of Orlando on March 4-5 at the Embassy Suites – Lake Buena Vista South (Orlando, FL) for the first time in 2015. Held at Florida’s high-tech corridor, LAM promises another no-hype look at […]
Direct Metal Deposition of Functional Graded Material
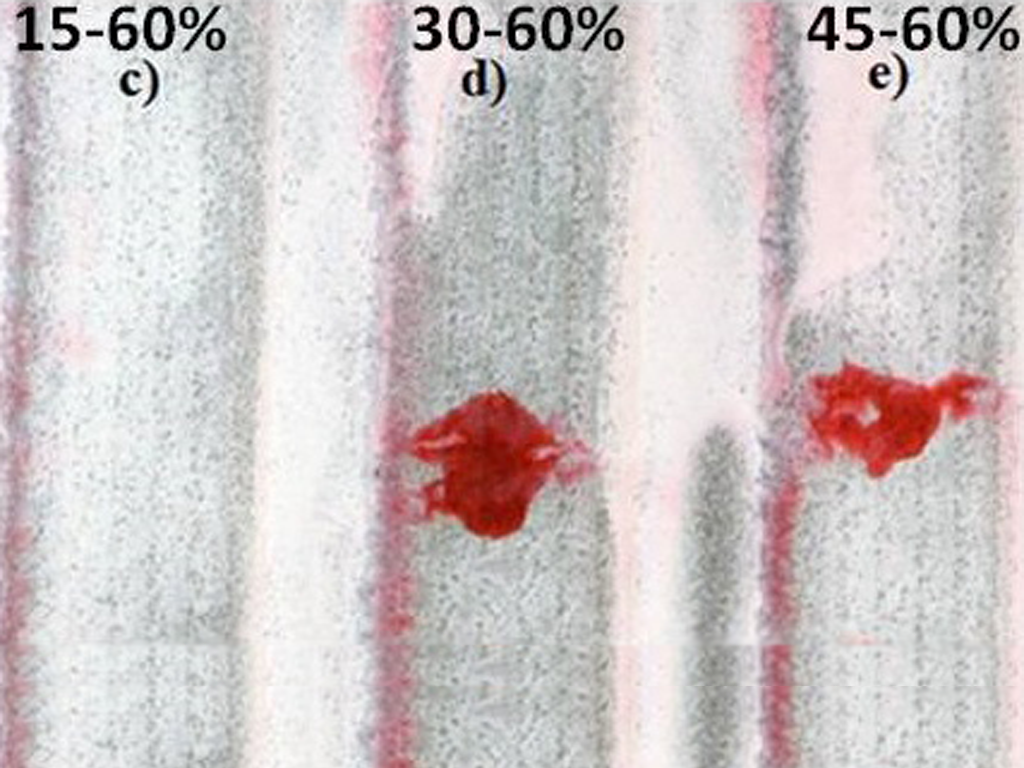
By J. M. Amado, J. N. Montero, M. J. Tobar, A. Yañez Functionally graded materials (FGM´s) are usually described as composite materials in which composition and structure varies gradually from one point to another. Traditional composites are based on homogeneous mixtures where the properties of the respective components are averaged according to their relative proportion. […]