By Chao Huang, Jimin Chen and Shi bai
Introduction
In recent years, glass has been widely used in different industrial field due to its excellent physical and chemical properties. However the glass cutting is always a difficulty because of its fracture characteristics. Especially in the field of irregular curve cutting, sloped cutting and drilling. In this study, we developed a so called “laser saw” technology. With this technology, the laser power for cutting thick glass could be significantly decreased. Not only can it cut irregular shape but also it can realize sloped cutting which means the cutting section is not perpendicular to the glass surface.
Glass Cutting
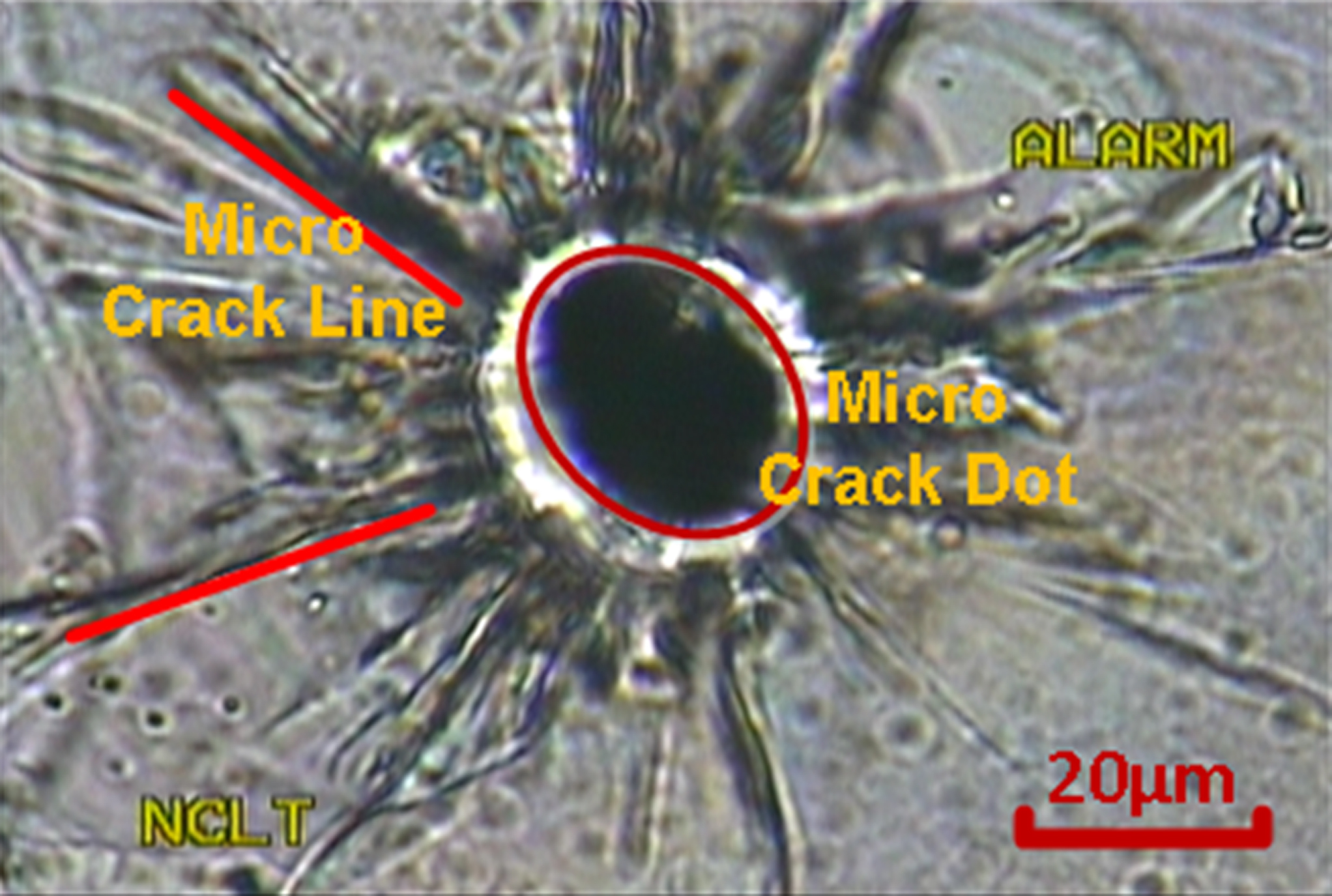
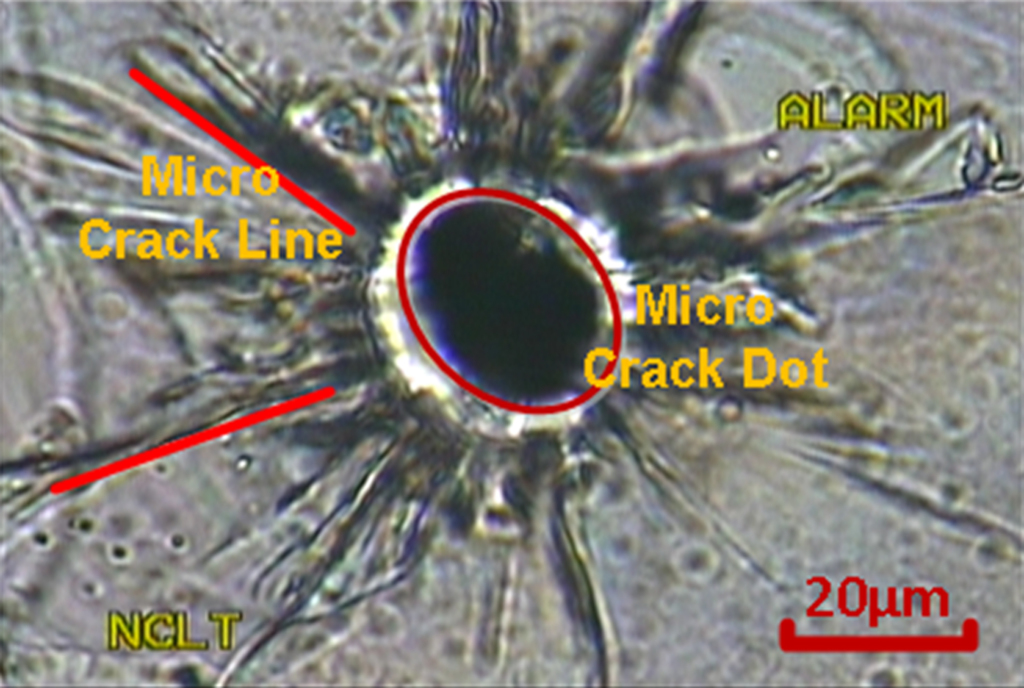
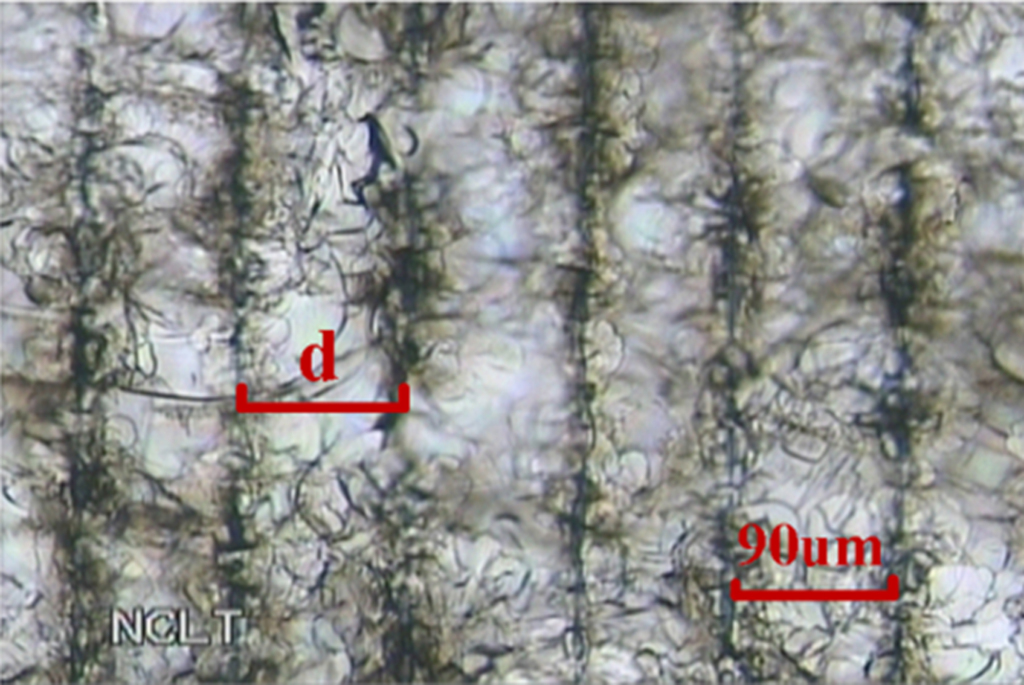
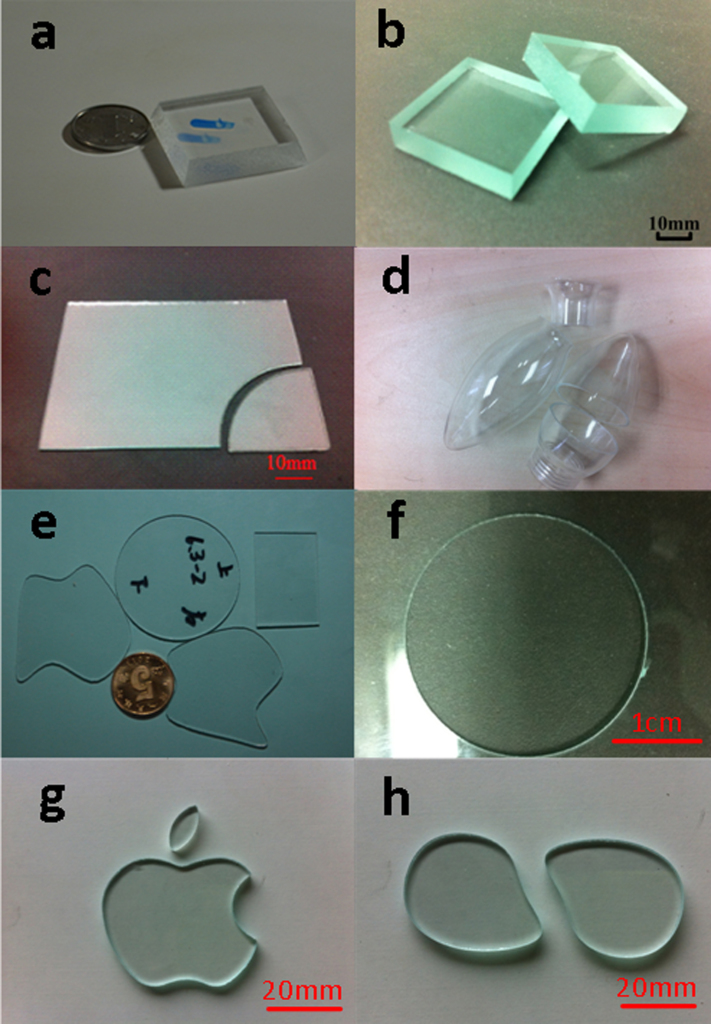
The focused pulse laser beam makes a reciprocating motion like a saw under the control of “laser saw” system. So that many micro crack dots were generated in the glass and they were connected to each other through the micro crack lines around dot, as is shown in Fig. 1. So that cutting face was generated in the glass (Fig. 2). For thin glass, it would be separated from the cutting face automatically. For the thick glass we exert a slight force on the glass to separate it.
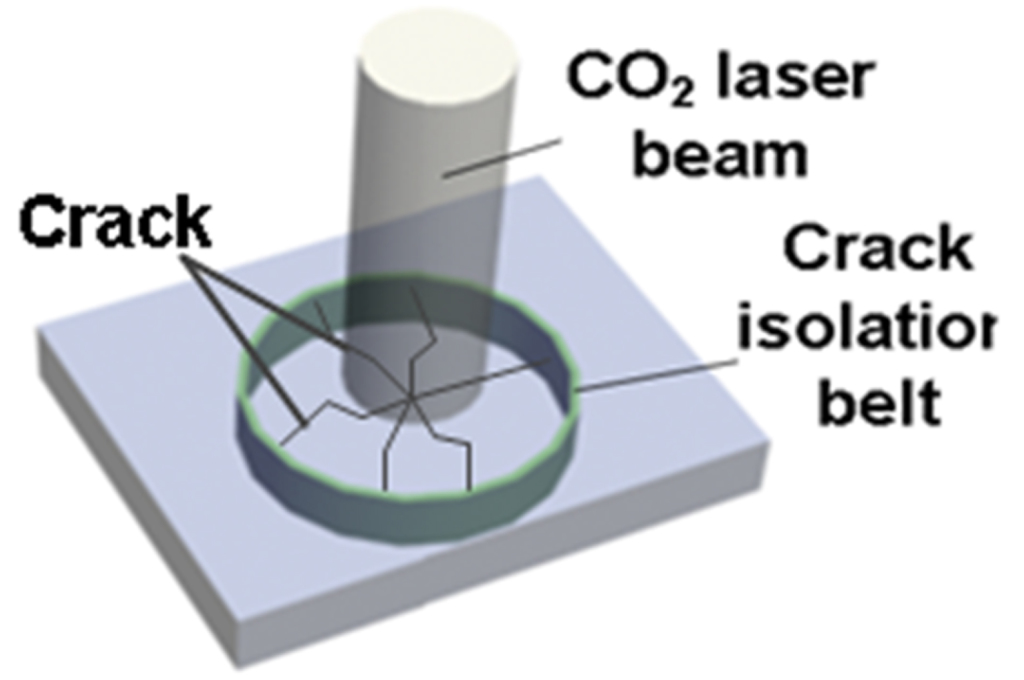
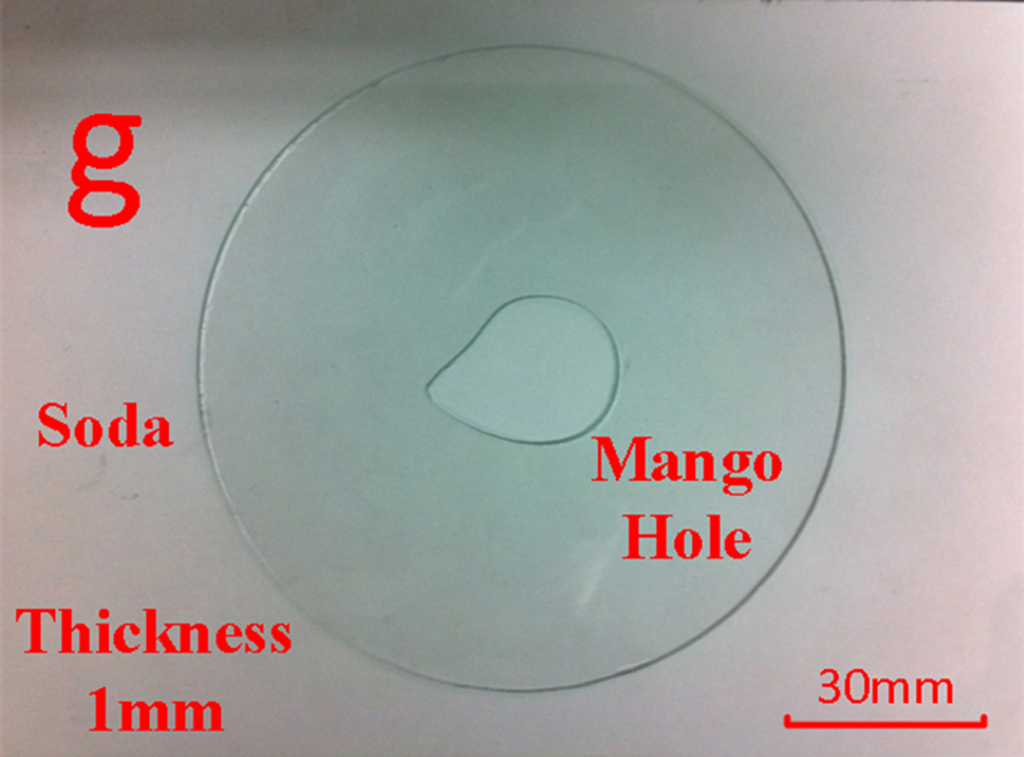
The irregular shape drilling can be realized by this method with a help of CO2 laser. First, we curve a series of micro crack dots by laser saw in the glass. These dots constitute an isolation belt. Then a CO2 laser is used to irradiate the area surrounded by the belt to break the glass. The isolation belt can stop the crack from passing, as is shown in Fig. 3. So the material surrounded by belt is removed and the surrounding material isn’t damaged. It has no need of a cutting feed path in this method for glass drilling. Fig. 4 is Mango shape hole in the 1 mm thickness soda lime glass.
Conclusions
With this laser saw a small power of laser is able to cut thick glass. It is the saw blade length to decide the cutting thickness rather than a laser power. The roughness of the cutting face is less than Ra 8 μm. With this saw, any shape of glass can be obtained under Computer Numerical Control (CNC) during cutting. Moreover, even the slope face can be achieved. We admit a lot of phenomena need further research. And the roughness, cutting speed need to be improved. In addition, according to the character of this method it might be suitable for metal cutting.





